NCLEX-RN Exam Guide
- What Is the NCLEX-RN?
- 2024 NCLEX-RN Pass Rates
- Registering for the NCLEX-RN Test
- The NCLEX-RN Examination Fees
- How Long is the NCLEX-RN Examination?
- How the Questions Will Appear on the NCLEX-RN Exam
- Basic Terms and Definitions Used on the NCLEX-RN
- Helpful Hints for Success on the NCLEX-RN Exam
- What Will Happen on the Day You Take Your NCLEX-RN Examination?
- Rules and Regulations of the NCLEX-RN Examination
- What To Do When You are Done with Your NCLEX RN Examination?
- What Kind of Questions Can I Expect to See on the NCLEX-RN Test?
- New Format NCLEX-RN Test Questions
- Distribution of the Four NCLEX-RN Test Categories
- Category 1: Safe and Effective Care Environment
- Category 2: Health Promotion and Maintenance
- Category 3: Psychosocial Integrity
- Category 4: Physiological Integrity
- Latest Articles & Guides

Welcome to RegisteredNursing.org's NCLEX-RN Review Guide. This guide gives you over 85 pages of expert-written guidance covering how and what you need to know to pass the NCLEX-RN exam successfully and become an RN.
Directly below is an accordion-style table of contents focusing now on the many topics and subcategories of the four main test categories. You can also use the navigation drop-down tool to the left to navigate the various sections of the guide. You’ll find test details, including how test questions are arranged, designed, and implemented. We also give expert advice on the day of experience, study tips, and tricks, as well as 200+ NCLEX-RN practice test questions with thorough rationales.
Passing this exam will allow RNs to advance in their career and enhance their education via programs such as RN to BSN or RN to MSN options.
Enjoy!
A. The Management of Care
- Advance Directives: NCLEX-RN
- Advocacy: NCLEX-RN
- Assignment, Delegation and Supervision: NCLEX-RN
- Case Management: NCLEX-RN
- Client Rights: NCLEX-RN
- Collaboration with Interdisciplinary Team: NCLEX-RN
- Concepts of Management: NCLEX-RN
- Confidentiality and Information Security: NCLEX-RN
- Continuity of Care: NCLEX-RN
- Establishing Priorities: NCLEX-RN
- Ethical Practice: NCLEX-RN
- Information Technology: NCLEX-RN
- Informed Consent: NCLEX-RN
- Legal Rights and Responsibilities: NCLEX-RN
- Performance Improvement & Risk Management: NCLEX-RN
- Referrals: NCLEX-RN
B. Safety & Infection Control
- Accident/Error and Incident Prevention: NCLEX-RN
- Emergency Response Plans: NCLEX-RN
- Ergonomic Principles: NCLEX-RN
- Handling Hazardous and Infectious Materials: NCLEX-RN
- Home Safety: NCLEX-RN
- Reporting Incident, Event, Irregular Occurrence, Variances: NCLEX-RN
- Safe Use of Equipment: NCLEX-RN
- Security Plans: NCLEX-RN
- Standard Precautions, Transmission Based, Surgical Asepsis: NCLEX-RN
- Use of Restraints and Safety Devices: NCLEX-RN
A. Aging Process
B. Anti/Intra/Postpartum & Newborn Care
C. Developmental Stages and Transitions
D. Health Promotion & Disease Prevention
E. Health Screening
F. High Risk Behaviors
G. Lifestyle Choices
H. Self Care
I. Techniques of Physical Assessment
A. Basic Care & Comfort
- Assistive Devices: NCLEX-RN
- Elimination: NCLEX-RN
- Mobility and Immobility: NCLEX-RN
- Non Pharmacological Comfort Interventions: NCLEX-RN
- Nutrition and Oral Hydration: NCLEX-RN
- Personal Hygiene: NCLEX-RN
- Rest and Sleep: NCLEX-RN
B. Pharmacological & Parenteral Therapies
- Adverse Effects, Contradictions, Side Effects and Interactions of Medications: NCLEX-RN
- Blood and Blood Products: NCLEX-RN
- Central Venous Access Devices: NCLEX-RN
- Dosage Calculations: NCLEX-RN
- Expected Actions and Outcomes: NCLEX-RN
- Medication Administration: NCLEX-RN
- Parenteral and Intravenous Therapies: NCLEX-RN
- Pharmacological Pain Management: NCLEX-RN
- Total Parenteral Nutrition (TPN): NCLEX-RN
C. Reduction of Risk Potential
- Changes and Abnormalities in Vital Signs: NCLEX-RN
- Diagnostic Tests: NCLEX-RN
- Laboratory Values: NCLEX-RN
- Potential for Alterations in Body Systems: NCLEX-RN
- Potential for Complications from Surgical Procedures and Health Alterations: NCLEX-RN
- Potential for Complications of Diagnostic Tests, Treatments, and Procedures: NCLEX-RN
- System Specific Assessments: NCLEX-RN
- Therapeutic Procedures: NCLEX-RN
D. Physiological Adaptation
What Is the NCLEX-RN?
According to the National Council of State Boards of Nursing, "Beliefs about people and nursing underlie the NCLEX-RN Test Plan. People are finite beings with varying capacities to function in society. They are unique individuals who have defined systems of daily living reflecting their values, motives, and lifestyles. People have the right to make decisions regarding their healthcare needs and to participate in meeting those needs. The nursing profession makes a unique contribution to helping clients (individual, family, or group) achieve an optimal level of health in various settings. For the NCLEX examination, a client is defined as an individual, family, or group that includes significant others and the population.
Nursing is both an art and a science, founded on a professional body of knowledge that integrates concepts from the liberal arts and the biological, physical, psychological, and social sciences. It is a learned profession based on knowledge of the human condition across the lifespan and an individual’s relationships with others and within the environment. Nursing is a dynamic, continually evolving discipline that employs critical thinking to integrate increasingly complex knowledge, skills, technologies, and client care activities into evidence-based nursing practice. The goal of nursing for client care is preventing illness and potential complications, protecting, promoting, restoring, and facilitating comfort, health, and dignity in dying.
The RN provides a unique, comprehensive assessment of the client’s health status, applying principles of ethics, client safety, health promotion, and the nursing process. The nurse then develops and implements an explicit plan of care. The nurse assists clients in promoting health, coping with health problems, adapting to and/or recovering from the effects of disease or injury, and supporting the right to a dignified death. The RN is accountable for abiding by all applicable member board jurisdiction statutes related to nursing practice."
2024 NCLEX-RN Pass Rates
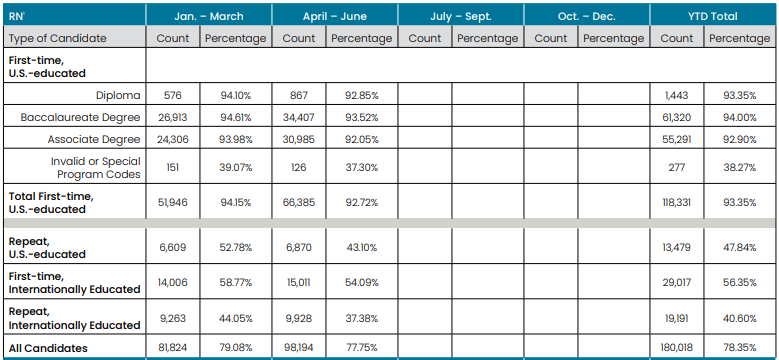
Source:
https://www.ncsbn.org/public-files/NCLEX_Stats_2024-Q2-Passrates.pdf
Past Years NCLEX-RN Pass Rates (First Time, US Educated)
- 2023 – 186,350 Takers, 88.56% Pass
- 2022 – 188,005 Takers, 79.90% Pass
- 2021 – 185,062 Takers, 82.48% Pass
- 2020 – 177,407 Takers, 86.57% Pass
- 2019 – 171,387 Takers, 88.18% Pass
- 2018 – 163,238 Takers, 88.29% Pass
- 2017 – 157,720 Takers, 87.11% Pass
- 2016 – 157,073 Takers, 84.57% Pass
- 2015 – 157,882 Takers, 84.53% Pass
- 2014 – 157,372 Takers, 81.78% Pass
- 2013 – 155,098 Takers, 83.04% Pass
Please note: The above numbers reflect first-time test taker pass rates.
Source: https://www.ncsbn.org/exams/exam-statistics-and-publications.page
Additional NCLEX-RN Facts & Figures by NCSBN
- 2023 NCLEX Fact Sheet
- 2022 NCLEX Fact Sheet
- 2021 NCLEX Fact Sheet
- 2020 NCLEX Fact Sheet
- 2019 NCLEX Fact Sheet
- 2018 NCLEX Fact Sheet
- 2017 NCLEX Fact Sheet
- 2016 NCLEX Fact Sheet
- 2015 NCLEX Fact Sheet
- 2014 NCLEX Fact Sheet
- 2013 NCLEX Fact Sheet
Registering for the NCLEX-RN Test
According to the National Council of State Boards of Nursing, Inc., all those who wish to take the NCLEX-RN Examination must:
- Apply for their registered professional nursing license with the state board of nursing where the person wants their initial license. For example, if you went to school in Pennsylvania and want to get your registered nursing license in Pennsylvania, you would apply for your registered professional nursing license with the Pennsylvania State Board of Nursing. On the other hand, if you went to school in Pennsylvania and want to get your registered professional nursing license in California, you would apply for your registered professional nursing license with the California State Board of Nursing. If, at a later date, you decide to work in another state after you get your initial registered professional nursing license, you can apply to that state for your registered professional nursing license without retaking the NCLEX-RN Examination because all states in our nation will give your registered professional nursing license with a process called reciprocity.
- You must meet the state's eligibility requirements to take the NCLEX-RN Examination.
- You then register for the NCLEX-RN Examination with Pearson VUE which is the official testing company. Your nursing school will give you this information and the necessary registration forms.
- You will then receive your NCLEX Registration Acknowledgement by email from Pearson VUE after the state board of nursing validates that you are eligible to take the NCLEX-RN Examination.
- The final step for registering for the NCLEX-RN Examination is scheduling the date and time of your examination with Pearson VUE and paying the fees for it.
If you have to change your testing appointment time for the NCLEX-RN Examination, you must change it by using the Pearson VUE website or by calling Pearson VUE but this must be done at least 24 hours before your scheduled test date and time.
For example, you must change your test time appointment by Friday at least 24 hours in advance of your appointment time, the local standard time when your examination is scheduled on a Saturday.
You can register for the NCLEX-RN Examination using a major credit card, such as VISA, MasterCard or American Express, by either registering at the Pearson VUE website or by contacting Pearson VUE by telephone. You MUST have an email address when you register regardless of whether you are registering by telephone or registering for the test at their website.
Please note that Pearson VUE will NOT send any information or registration acknowledgments via the US Postal Service. They only send this information by email so it is your responsibility to have access to the internet and your email.
The NCLEX-RN Examination Fees
The basic registration fee for the NCLEX-RN Examination is $200.00. Additional fees are required if you change the state board of nursing that you want to apply to after you have registered or change the language you choose for the examination.
There are NO refunds of these fees for any reason.
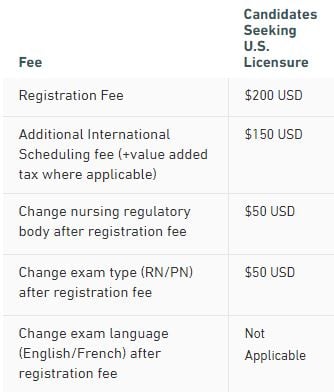
Source: https://www.nclex.com/fees-payment.page
How Long is the NCLEX-RN Examination?
The NCLEX-RN Examination is a variable-length computerized adaptive test. It is not offered in paper-and-pencil or oral examination formats.
You may have to take anywhere from 75 to 265 questions depending on how you are doing with answering the questions on the test.
Of the 75 to 265 questions on the test, 15 of these questions are pretest questions. These 15 pretest questions will not be scored and they will NOT be part of or included in your final test score on your NCLEX-RN Examination.
You will have up to a maximum of 6 hours to complete the NCLEX-RN Examination regardless of the number of questions that you will have to answer on this examination.
This total of 6 hours includes:
- A short instructional tutorial about the examination that you will be taking.
- Two pre-programmed optional breaks which you may or may not choose to take. One of these two optional breaks is pre-programmed 2 hours after the test began and the other optional break is pre-programmed for 3.5 hours after the test began. The computer will alert you went these pre-programmed breaks are due.
- Other breaks that you choose to take AND
- Answering all of the questions on your NCLEX-RN Examination regardless of the number of questions that you have to do up to 265 questions on the test.
After you have answered your minimum number of questions, as based on how you have done on the examination, the testing will stop because the test taker is either above or below the passing standard. In other words, the test will stop when you have passed and the test will also stop when it is certain, or almost certain, that you have not passed the NCLEX-RN Examination.
The test will also stop when all the questions are done and also when the 6-hour time limit for the entire examination is over and done.
Based on this information, it is in your best interest to maintain a reasonable pace during the test and take no more than one or two minutes on each question. Keep in mind that you may need the full 6 hours when you have to take all of the available questions for your examination which can number up to 265 questions.
How the Questions Will Appear on the NCLEX-RN Exam
You will get only one question at a time on your computer screen. You can read the question and think about it as long as you like but the question must be answered before you can go on to the next examination question. You must, therefore, answer the question even when you are not certain and not sure that your answer is correct or the test will not proceed to the next question.
Do not waste time on a question; give it your best try. Wild guessing is NOT advised. Select the answer that you believe is the best choice and then move on to your next question.
So, read the question carefully, think about it and then answer it with your best possible response even when you are not sure. Do not get stuck on it. Remember, you only have 6 hours to finish the entire test. Keep up a reasonable and consistent pace as you go through the NCLEX-RN Examination towards its completion.
Basic Terms and Definitions Used on the NCLEX-RN
Now you will learn how to define some of the basic terms and definitions that you will see on the NCLEX-RN Examination.
When you see the word "client", it is the same as the patient and the word client can also refer to an individual, a family, or a group.
A "group" is more than one client or patient. Groups can be defined as populations of people, age groups of people, and other groups of people.
NCLEX-RN Integrated Processes are those processes that are recurring themes in nursing and the nursing process. The integrated processes that you will see on your NCLEX-RN Examination are the Nursing Process, Caring, Communication and Documentation, and lastly Teaching and Learning. You will learn about all of these integrated processes during this NCLEX review course.
The word "prescription" is defined as an order, intervention, remedy, or treatment ordered or directed by an authorized health care provider such as a doctor, nurse practitioner, and a physician extender like a physician's assistant.
The term "exhibit" indicates that you will see some pictures or diagrams such as a client chart or medical record.
Helpful Hints for Success on the NCLEX-RN Exam
The most important thing that you must bring with you when you go to take your NCLEX-RN Examination is your self-confidence.
You would never have been able to complete your nursing program and graduate from your school if you did not have great good grades and deep knowledge and understanding of nursing and nursing care.
You have the knowledge to pass and ace the NCLEX-RN Examination so take your test with confidence!
See our 10 tips for preparing for the NCLEX-RN and Top NCLEX review courses available.
What Will Happen on the Day You Take Your NCLEX-RN Examination?
In addition to your confidence and a well-rested body and mind, you must also bring personal identification that has your name which fully matches the name that you registered for the test, a recent photograph, AND your signature.
This personal identification can include your current driver's license, a state identification card, a military identification card, a passport, or a permanent resident card with your recent photo; your full name, and your signature. You will not be allowed to your the NCLEX-RN Examination if your personal identification does not fulfill these mandated requirements. Additionally, you will also have to begin and pay the fees for the application process all over again.
You should also bring no or as few as possible, personal items to your testing site. When you arrive at your testing site you will be told to put all of these personal items into a locker. No personal items at all are allowed to be brought into the testing area and the test administrators are not responsible for any lost items so bring as little as possible into the testing center. The only thing that you really need when you go to your testing site is your personal identification.
A formal check-in process is done by the test administrators when you arrive at your testing center. This formal check-in process requires that you:
- Give your valid and acceptable form of personal identification to the test administrator so that they can check and validate your identity.
- Provide your digital signature and your palm vein scan to the test administrator.
- Have your photograph taken by the testing site administrator.
You will be asked to remove any jewelry, watches, and outer clothing such as a coat or hat.
After this formal check-in process and identity validation, the testing site administrator will give you brief instructions and then bring you to your seat with your assigned computer that you will use for the entire test. You may not leave this seat for any reason unless you request and are granted permission to leave this seat for a break.
Arrive at least .5 hours before your scheduled testing time. Allow enough time for inclement weather and traffic jams. If you are not sure of how to get to your assigned testing center, do a practice drive several days before your test.
Your Assigned Seat in The Testing Room
The testing room will be comfortable with an environmental temperature that is regulated with heat during the colder winter months and air conditioning during warmer weather. The testing room will be sparse and quiet. NO talking and conversations are permitted, however, there may be sounds and noises that you may find distracting to you. For example, you may hear typing, coughs, and/or sneezes.
Not all the test-takers in the testing room are tasking the NCLEX RN examination; some of these other test-takers may have to type essay answers which you may find distracting.
Ask the test administrator for earplugs to block out these distracting noises if you think that you will be distracted by extraneous noises in the testing room.
Rules and Regulations of the NCLEX-RN Examination
You must be 100% aware of and compliant with all the rules and regulations relating to taking your NCLEX-RN Examination. A failure to comply with any rule is grounds for dismissal from the examination.
You may NOT:
- Attempt to take the NCLEX-RN Examination for someone else.
- Tamper with your assigned computer in any way.
- Jot down or write on anything except the erasable note board which was given to you by the test administrator at the testing site when you arrived.
- Get any personal items from your locker during the entire time of the examination and during your breaks.
- Talk about test questions with anyone.
- Attempt to mentally recall any test questions using your memory.
- Cheat, ask for the help of another or give help to another test taker.
- Use your computer for anything other than your NCLEX-RN Examination.
Other rules and regulations for the examination state that you MUST:
- Raise your hand to ask the test administrator for a clean note board if you need it.
- Raise your hand to ask the test administrator for a break and then only take the break when you have been given permission by the test administrator to do so. A palm vein scan will be taken when you leave the room for a break and, again, when you re-enter the testing room.
- Raise your hand to ask the test administrator for another computer when there is a problem with your assigned computer.
- Return the note board when you leave the testing room.
- Use the earphones that were given to you by the testing administrator. You may not use your own.
- Use the earplugs provided by the test administrator when you have requested them.
- Raise your hand to tell the test administrator that you are done with your examination.
What To Do When You are Done with Your NCLEX RN Examination?
When you are done with your NCLEX RN Examination, you will get a short survey questionnaire that will ask you about the experiences that you have had when checking into the testing site and during the entire time that you were in the testing center and the testing room.
Raise your hand when you are done with this brief questionnaire to let the test administrator know that you have completed your NCLEX RN Examination. The test administrator will collect all the things that you were given by a testing administrator such as your earphones and your note board.
RELATED: How Many Times Can You Take the NCLEX-RN Exam?
What Kind of Questions Can I Expect to See on the NCLEX-RN Test?
You will see different levels of questions on the NCLEX-RN Examination.
The levels of questions on the NCLEX-RN Examination include knowledge and recall, comprehension of the material, application of the material into nursing practice, and higher levels of the cognitive domain of nursing.
The practice of nursing requires the application of knowledge, skills, and abilities in all aspects of nursing care; therefore, the majority of items are written at the application or higher levels of cognitive ability.
Knowledge and recall questions are the simplest of all the types of questions that you will get on the NCLEX examination.
An example of a knowledge and recall question is:
- You should respond to the couple by stating that only unanticipated treatments and procedures that are not included in the advance directive can be made by the legally appointed durable power of attorney for healthcare decisions.
- You should be aware of the fact that the wife of the client has a knowledge deficit relating to advance directives and durable powers of attorney for healthcare decisions and plan an educational activity to meet this learning need.
- You should be aware of the fact that the client has a knowledge deficit relating to advance directives and durable powers of attorney for healthcare decisions and plan an educational activity to meet this learning need.
- You should reinforce the wife’s belief that legally married spouses automatically serve for the other spouse’s durable power of attorney for health care decisions and that others than the spouse cannot be legally appointed while people are married
Correct Response: A
You should respond to the couple by stating that only unanticipated treatments and procedures that are not included in the advance directive can be made by the legally appointed durable power of attorney for healthcare decisions.
Both the client and the client’s spouse have knowledge deficits relating to advance directives. Legally married spouses do not automatically serve for the other spouse’s durable power of attorney for health care decisions; others than the spouse can be legally appointed while people are married.
Now, here is another knowledge and recall question.
Who is a nurse who worked with the wounded during the Crimean War?
- Martha Washington
- Dolly Madison
- Dorothea Orem
- Florence Nightingale
The answer to this question is D, Florence Nightingale. Florence Nightingale cared for the wounded soldiers of the Crimean War. Again, this question is rather simple; it just tests your ability to remember facts that you have learned.
Comprehension questions test your ability to apply a principle to a situation. Now, let's try a comprehension-level question.
Proper handwashing ensures:
- Breaking the mode of transmission.
- Skin sterility.
- Surgical asepsis.
- Skin integrity.
The answer to this question is A, breaking the mode of transmission. In this question, you had to apply the principles of infection control to proper handwashing.
Now, here is another comprehension-level question.
What type of asepsis is used for the administration of topical medications?
- Medication asepsis
- Surgical asepsis
- Sterile asepsis
- Medical asepsis
The correct response is D, medical asepsis. Medical asepsis is used for the administration of topical medications. In this comprehension question, you are demonstrating your comprehension of the principles of medical and surgical asepsis and medication administration.
Application questions test your ability to apply your knowledge to practice.
You live in your home with your husband and two children. What is the first thing you should do when the smoke alarms in your house start to go off?
- Evacuate family members.
- Dial 911.
- Run from the home.
- Use an A type fire extinguisher.
The correct answer is A, the first thing that you should do is to evacuate all members of the family. This application question tests your ability to apply the principles of fire safety and RACE to a current situation.
Now, try this one.
You are caring for a seven-year-old boy in the hospital. You have noticed that the boy is wetting his pants during the daytime hours when he is awake. What should you do?
- Admonish the boy.
- Understand that the boy is regressing.
- Understand that the boy is repressing.
- Ignore it.
The correct answer is B, you should understand that this boy is regressing during this stressful hospitalization. With this question, you have applied the principles of mental health and defense mechanisms to a patient situation.
New Format NCLEX-RN Test Questions
In the past, all of the NCLEX-RN examination questions were only multiple-choice questions with only four choices from which the correct choice had to be selected. Now, these four choices multiple-choice questions are still on the examination, however, new format questions have been recently added.
Fortunately, the majority of the NCLEX-RN examination questions are still the traditional four-option multiple-choice questions but be prepared for alternate format questions.
All of the questions that I just discussed for the knowledge and recall, comprehension, and application levels were all traditional four-choice multiple-choice questions.
Most of the four-choice multiple-choice questions are narrative-type questions like the ones above, but others can consist of audio clips, tables, charts, graphs, patient medical records, and images or pictures. For example, you may get a four-choice multiple-choice question that asks you to select an anatomical body part from a graphic image of the body; you may also get a four-choice multiple-choice question that asks you to select a heart or breath sound that you hear with an audio clip by using your earphones. For example, you may hear a particular breath sound and you will then be asked the name of this abnormal breath sound.
The alternative and new format questions can also consist of tables, charts, graphs, audio clips, and images or pictures, in addition to narrative questions.
The alternative and new format questions are:
Multiple response questions that ask you to select ALL the responses or items in the question that are correct. With this type of alternative and new format question, you will have to select more than one correct answer.
You will not get any credit for a question if you do not answer with ALL of the possible correct answers. For example, you will not get any credit for the question if you only choose three of the four correct answers. There is NO partial credit for questions on the NCLEX examination. Each question is graded as correct or incorrect.
- Fill in the blank questions that ask you to fill in the correct answer to a calculation that you must mathematically calculate.
- Hot spot questions ask you to find and click on the "hot spot" or the specific area that shows the spot that the question is asking you to identify.
- Ordered response questions that ask you to use the computer mouse and then drag and drop items on a list in the correct sequential order.
All question types, including the traditional four-item multiple choice questions, and all of these alternatives, new format questions may include multimedia, such as charts, tables, graphics, sound, and video.
Now, let's do several multiple-response questions. Remember, you must select all the correct responses in order to get these questions correct. You will be graded incorrectly if you miss even one correct response.
Which of the following sports are NOT considered contact sports? Select all that apply.
- Tennis
- Football
- Boxing
- Golf
- Basketball
- Diving
- Rugby
The correct responses to this question are A, D, E, and F, tennis, golf, basketball, and diving are NOT contact sports. Football, boxing, and rugby are considered contact sports. If you only selected three responses instead of the correct four choices, you would not get any credit for this question; this question will be scored as incorrect because you missed one or more of the four correct responses.
Now let's do a couple more multiple-response questions.
You are working the evening shift and your hospital is alerted to the fact that a cyclone is possibly heading to your nursing home. What should you do? Select all that apply.
- Evacuate bedridden patients to a lower level using an elevator.
- Evacuate patients to a higher floor.
- Cover the patients with wet blankets.
- Move patients to a hallway area that is not near any windows.
- Lower the beds of bedridden patients to the lowest possible height.
- Close all of the window drapes and curtains.
The correct responses to this question are D, E, and F
These emergency interventions protect patients from flying glass and other debris that can occur with a cyclone. Again, if you only got two of these three responses, you will not get any credit for this question. It will be scored incorrectly because you missed one of the correct responses.
Now, let's try this multiple-response question:
Which of these are a role and responsibilities of a registered nurse in terms of an internal disaster? Select all that apply.
- Participating in all internal emergency preparedness disaster drills
- Using autocratic and authoritarian leadership skills
- Establishing those urgent clients is the greatest triage priority
- Communicating with family members about the patient's status
The correct responses to this question are A, B, C, and D
Again, if you only got three or fewer of these four responses, you would not get any credit for this question.
Fill in the blanks questions are used for calculations, such as the ones that you do for medication dosages and intravenous fluid flow rates.
For example:
How many mLs are there in 10 ounces? Fill in the blank.
The correct answer is 300 mLs. There are 30 mLs in one ounce so 30 x 10 = 300
Any answer other than 300 mLs is incorrect.
You are using an intravenous set that has a drop factor of fifteen drops per mL. How many drops per minute will you administer when the doctor has ordered 100 mLs per hour? Fill in the blank.
The correct response is 25 drops per minute.
All answers other than 25 drops per minute are incorrect.
Now, here is your last fill-in-the-blank practice question.
You have to administer 3,000 units of heparin subcutaneously and the label on the heparin bottle reads 4,000 units per mL. How many mLs will you administer? Fill in the blank:
The correct answer is 0.75 ccs or mLs. The answer is calculated by dividing 3,000 units of heparin by 4,000 which is 0.75.
Ordered response questions ask you to use the computer mouse and then drag and drop items on a list in correct sequential order.
For example:
Place the following phases of the Nursing Process in the correct sequential order:
- Planning
- Nursing diagnosis
- Evaluation
- Implementation
- Assessment
For this question on the NCLEX-PN examination, you would drag and drop assessment to the top of the list because the assessment is the first phase of the nursing process; you would then you would drag and drop the following other phases of the Nursing Process in this order:
- Assessment
- Nursing diagnosis
- Planning
- Implementation
- Evaluation
Place these phases of the pharmacokinetic process in the correct sequential order:
- Distribution
- Absorption
- Excretion
- Metabolism
For this question you would drag and drop absorption to the top of the list because this is the first phase of the pharmacokinetic process; you would then drag and drop the following in this sequential order:
- Absorption
- Metabolism
- Distribution
- Excretion
Hot spots can include anatomical pictures which would require you to identify specific points in these pictures. Hot spot questions that could be included on your NCLEX-RN
An examination may be asked to identify:
- The umbilical vein
- The umbilical artery
- The correct placement of an ostomy pouch
- Parts of the brain
- Areas where you would place your stethoscope to hear a specific heart sound
- ECG lead placement spots
- Areas of the body where you would palpate for various pulses
- The male and female reproductive internal and external organs
Video questions on the NCLEX-PN Examination can include things like a patient scenario that you would view and then think about in order to answer a question. For example, a video may show you a nurse washing their hands. You may then be asked to identify the aspect of handwashing that the nurse did not do correctly.
When you watch a video, pay very close attention to all the details of what you see on the video.
Audio questions will instruct you to put your earphones on and listen to an audio segment. Breath and heart sounds as well as bowel sounds could be tested.
Some of the sounds that you may hear with these audio clips (COMING SOON!) are normal and abnormal breath sounds such as:
- Vesicular breath sounds
- Crackles or fine rales
- Crackles or coarse rales
- Wheeze
- Rhonchi
- Bronchial breath sounds
- Pleural Rubs
- Bronchovesicular breath sounds
You may also hear audio clips of heart sounds such as:
- A regular sinus beat
- An irregular heart rate
- A murmur
- Tachycardia
- Bradycardia
- S 1
- S 2
- S 3
- S 4
Distribution of the Four NCLEX-RN Test Categories
The NCLEX-RN Test Plan is organized into four major Client Needs categories. Two of the four categories are divided into subcategories as shown below:
- Safe and Effective Care Environment
- Management of Care – 17% to 23%
- Safety and Infection Control – 9% to 15%
- Health Promotion and Maintenance – 6% to 12%
- Psychosocial Integrity – 6% to 12%
- Physiological Integrity
- Basic Care and Comfort – 6% to 12%
- Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies – 12% to 18%
- Reduction of Risk Potential – 9% to 15%
- Physiological Adaptation – 11% to 17%
Category 1: Safe and Effective Care Environment
The Safe and Effective Care Environment consists of the Management of Care and the Safety and Infection Control subcategories.
Management of Care
The registered nurse provides and directs nursing care that enhances the care delivery setting to protect the client and health care personnel.
RNs must be able to:
- Integrate advance directives into client plan of care
- Assign and supervise the care provided by others (e.g., LPN/LVN, assistive personnel, other RNs)
- Organize workload to manage time effectively
- Participate in providing cost-effective care
- Initiate, evaluate, and update the plan of care (e.g., care map, clinical pathway)
- Provide education to clients and staff about client rights and responsibilities
- Advocate for client rights and needs
- Collaborate with health care members in other disciplines when providing client care
- Manage conflict among clients and health care staff
- Maintain client confidentiality and privacy
- Provide and receive a report on assigned clients (e.g., standardized handoff communication)
- Use approved abbreviations and standard terminology when documenting care
- Perform procedures necessary to safely admit, transfer or discharge a client
- Prioritize the delivery of client care
- Recognize ethical dilemmas and take appropriate action
- Practice in a manner consistent with a code of ethics for registered nurses
- Verify that the client comprehends and consents to care and procedures
- Receive and/or transcribe health care provider orders
- Utilize information resources to enhance the care provided to a client (e.g., evidenced-based research, information technology, policies, and procedures)
- Recognize the limitations of self/others and seek assistance
- Report client conditions as required by law (e.g., abuse/neglect, communicable disease, gunshot wound)
- Report unsafe practices of health care personnel and intervene as appropriate (e.g., substance abuse, improper care, staffing practices)
- Provide care within the legal scope of practice
- Participate in performance improvement/quality improvement process and
- Recognize the need for referrals and obtain necessary orders
Related content includes, but is not limited to:
- Advance Directives
- Advocacy
- Assignment, Delegation, and Supervision
- Case Management
- Client Rights
- Collaboration with Interdisciplinary Team
- Concepts of Management
- Confidentiality/Information Security
- Continuity of Care
- Establishing Priorities
- Ethical Practice
- Informed Consent
- Information Technology
- Legal Rights and Responsibilities
- Performance Improvement & Risk Management (Quality Improvement)
- Referrals
Explore – Management of Care Practice Test Questions
All of these content areas will be reviewed above for the Management of Care portion of this NCLEX-RN review in a similar manner to how this review will cover all of the other NCLEX-RN examination content areas as established by the National Council of the State Boards of Nursing.
Safety and Infection Control
The registered nurse protects clients and health care personnel from health and environmental hazards.
They must be able to:
- Assess the client for allergies and intervene as needed (e.g., food, latex, environmental allergies)
- Protect client from injury (e.g., falls, electrical hazards)
- Ensure proper identification of client when providing care
- Verify the appropriateness and/or accuracy of a treatment order
- Implement emergency response plans (e.g., internal/external disaster)
- Use ergonomic principles when providing care (e.g., assistive devices, proper lifting)
- Follow procedures for handling biohazardous materials
- Educate client on home safety issues
- Acknowledge and document practice errors (e.g. incident report for medication error)
- Facilitate appropriate and safe use of equipment
- Participate in institution security plan (e.g., newborn nursery security, bomb threats)
- Apply principles of infection control (e.g., hand hygiene, surgical asepsis, isolation, sterile technique, universal/standard precautions)
- Educate client and staff regarding infection control measures
- Follow requirements for use of restraints and/or safety devices (e.g., least restrictive restraints, timed client monitoring)
Related content includes, but is not limited to:
- Accident/Error and Incident Prevention
- Emergency Response Plans
- Ergonomic Principles
- Handling Hazardous and Infectious Materials
- Home Safety
- Reporting Incident / Event / Irregular Occurrence / Variances
- Safe Use of Equipment
- Security Plans
- Standard Precautions/Transmission Based Precautions/Surgical Asepsis
- Use of Restraints/Safety Devices
Explore – Safety & Infection Control Practice Test Questions
Category 2: Health Promotion and Maintenance
In this section, the registered nurse provides and directs nursing care to the client that incorporates knowledge of expected growth and development principles; prevention and/or early detection of health problems; and strategies to achieve optimal health.
They must be able to:
- Provide care and education for the newborn less than 1-month-old through the infant or toddler client through 2 years
- Provide care and education for the preschool, school-age and adolescent clients ages 3 through 17 years
- Provide care and education for the adult client aged 18 through 64 years
- Provide care and education for the adult client aged 65 through 85 years and over
- Provide prenatal care and education
- Provide care to the client in labor
- Provide post-partum care and education
- Assess and teach clients about health risks based on family, population, and/or community characteristics
- Assess the client's readiness to learn, learning preferences, and barriers to learning
- Plan and/or participate in community health education
- Provide information about health promotion and maintenance recommendations (e.g., physician visits, immunizations)
- Perform targeted screening assessments (e.g., vision, hearing, nutrition)
- Provide information for the prevention and treatment of high-risk health behaviors (e.g., smoking cessation, safe sexual practices, drug education)
- Assess the client’s ability to manage care in the home environment and plan care accordingly (e.g. equipment, community resources)
- Perform a comprehensive health assessment
Related content includes, but is not limited to:
- Aging Process
- Anti/Intra/Postpartum and Newborn Care
- Developmental Stages and Transitions
- Health Promotion/Disease Prevention
- Health Screening
- High-Risk Behaviors
- Lifestyle Choices
- Self Care
- Techniques of Physical Assessment
Explore – Health Promotion & Maintenance Practice Test Questions
Category 3: Psychosocial Integrity
In the Psychosocial Integrity part of your examination, you will be expected to demonstrate the knowledge and skills necessary to provide and direct nursing care that promotes and supports the emotional, mental and social well-being of the client experiencing stressful events, as well as clients with acute or chronic mental illness.
The nurse is expected to be able to:
- Assess the client for abuse or neglect and intervene as appropriate
- Incorporate behavioral management techniques when caring for a client (e.g., positive reinforcement, setting limits)
- Assess client for drug/alcohol dependencies, withdrawal, or toxicities and intervene as appropriate
- Assess client in coping with life changes and provide support
- Assess the potential for violence and use safety precautions (e.g., suicide, homicide, self-destructive behavior)
- Incorporate client cultural practices and beliefs when planning and providing care
- Provide end-of-life care and education to clients
- Assess family dynamics to determine the plan of care (e.g., structure, bonding, communication, boundaries, coping mechanisms)
- Provide care and education for acute and chronic behavioral health issues (e.g., anxiety, depression, dementia, eating disorders)
- Assess psychosocial, spiritual, and occupational factors affecting care, and plan interventions
- Provide care for a client experiencing visual, auditory, or cognitive distortions (e.g., hallucinations)
- Recognize non-verbal cues to physical and/or psychological stressors
- Use therapeutic communication techniques to provide client support
- Provide a therapeutic environment for clients with emotional/behavioral issues
The term mental health can have many definitions. For example, mental health can be defined as successful adjustments and coping with the stressors of everyday life in a manner that is acceptable to society and healthy for the client. On the other hand, mental illness can be defined as a lack of a person's adhering to society's norms and acting in a way that is not appropriate in terms of the client's behavior.
Some of the factors that impact the development of mental health include our inherited genetic make of one's life circumstances, such as good physical health, economic security, social support networks and friends, and nurturing during the early years of life as well as those described below.
Populations at Risk For Psychological Disorders Along the Life Span
Older adults may be at risk for a lack of psychological integrity as the result of social isolation, grief/loss after the death of a spouse, friend, or another loved one, fear of declining physical and mental abilities, actual physical and mental declines, and reduced income, for example.
Adolescents and young adults are often adversely affected by sexual identity issues, an eating disorder, peer pressure, illicit drug use, and bullying.
New parents often experience stressors relating to the transition from being a couple to being parents with great responsibilities, a possible loss of financial income, anxiety regarding the child's wellbeing, concerns that they are not adequate parents, coping with the baby's constant demands and needs, as well as some conflicts and ambivalence about accepting the pregnancy and the newborn.
Gender-Related Risk Factors
Women are at risk for mental illness as the result of domestic violence, hormonal changes as occur after pregnancy and menopause, internal, and intrapersonal conflicts about the multiple and challenging roles they wish, or have, to fulfill, including that of a full-time career person, homemaker, single parent, and the caregiver for the elderly parents.
Males may be adversely affected by economic and income concerns, the loss of sexual functioning, and declining muscular strength and stamina.
Risk Factors Secondary to Physical and Cognitive Illnesses and Disorders
The physically and cognitively impaired are at risk for mental illness because they are often affected by poor quality of life, impaired self-image, social isolation, a decreasing lack of independence, societal stigma, and a lack of meaningful relationships.
Social Risk Factors
The homeless, the indigent, and refugees have stressors such as financial uncertainty, poverty, poor social status, the loss of self-esteem and self-worth, and other stressors.
Commonly occurring signs and symptoms of mental illness are not always as clear, unambiguous, and objective as the signs and symptoms of a physiological disorder. Generally speaking, the signs and symptoms of mental disease can include social withdrawal, changes in personal habits like grooming and hygiene, abnormal changes in mood, changes in thought processes, and other behaviors.
The American Psychiatric Association's (APA) Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) contains four major categories of mental illness. Each of these four major categories contains many mental health disorders.
The APA's four major categories of mental health disorders are:
- Thought disorders: Thought disorders are characterized by disordered thoughts, feelings, and behaviors.
- Mood disorders: Mood disorders, also referred to as mood affective disorders, have an effect on the client's mood and affect. For example, the patient's mood can be happy, elated, somber, sad, depressed, or flat and without any emotion whatsoever.
- Behavioral disorders: Behavioral disorders can manifest with hostility, aggression, self-harm, harm to others, and defiance.
- Mixed disorders: Mixed disorders have to define characteristics, signs, and symptoms of more than one of the above APA categories of mental health disorders.
Mental health disorders can also be categorized and described as:
- Sexual disorders
- Gender identity disorders
- Cognitive disorders like delirium, dementia, and Alzheimer's disease
- Poor impulse control disorders
- Substance abuse disorders such as alcohol and illicit drug abuse, dependency, and addiction
- Anxiety disorders, such as obsessive disorders, phobias, and panic disorders
- Sleep disorders
- Eating disorders like anorexia nervosa
- Mood disorders like depression and bipolar disease
- Schizophrenia includes paranoid or catatonic-type schizophrenia
- Personality disorders like a dependent personality and an antisocial personality
Related content includes, but is not limited to:
- Abuse and Neglect
- Behavioral Interventions
- Chemical and Other Dependencies and Substance Abuse Disorders
- Coping Mechanisms
- Crisis Intervention
- Cultural Awareness and Influences on Health
- End of Life Care
- Family Dynamics
- Grief and Loss
- Mental Health Concepts
- Religious and Spiritual Influences on Health
- Sensory/Perceptual Alterations
- Stress Management
- Support Systems
- Therapeutic Communication
- The Therapeutic Environment
Explore – Psychosocial Integrity Practice Test Questions
Category 4: Physiological Integrity
In the Physiological Integrity part of your examination, you will be expected to demonstrate the knowledge and skills necessary to promote physical health and wellness by providing care and comfort, reducing client risk potential, and managing health alterations.
The four subsections under Physiological Integrity are Basic Care and Comfort, Pharmacological Therapies, the Reduction of Risk Potential, and Physiological Adaptation.
Basic Care and Comfort
In the Basic Care and Comfort questions, the nurse will be required to demonstrate that they can provide comfort and assistance in the performance of activities of daily living.
The nurse must be competent to:
- Assist the client to compensate for a physical or sensory impairment (e.g., assistive devices, positioning, compensatory techniques)
- Assess and manage a client with an alteration in elimination (e.g., bowel, urinary)
- Perform irrigations (e.g., of the bladder, ear, eye)
- Perform skin assessment and implement measures to maintain skin integrity and prevent skin breakdown (e.g., turning, repositioning, pressure-relieving support surfaces)
- Apply, maintain or remove orthopedic devices (e.g., traction, splints, braces, casts)
- Apply and maintain devices used to promote venous return (e.g., anti-embolic stockings, sequential compression devices)
- Implement measures to promote circulation (e.g., active or passive range of motion, positioning, and mobilization)
- Assess client need for pain management
- Provide non-pharmacological comfort measures
- Manage the client's nutritional intake (e.g., adjust diet, monitor height, and weight)
- Provide client nutrition through continuous or intermittent tube feedings
- Evaluate client intake and output and intervene as needed
- Assess and intervene in client performance of activities of daily living
- Perform post-mortem care
- Assess the client’s need for sleep/rest and intervene as needed
Related content includes but is not limited to:
- Assistive Devices
- Elimination
- Mobility/Immobility
- Non-Pharmacological Comfort Interventions
- Nutrition and Oral Hydration
- Personal Hygiene
- Rest and Sleep
Explore – Basic Care & Comfort Practice Test Questions
Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
The registered nurse provides care related to the administration of medications and parenteral therapies.
Registered nurses must be able to:
- Administer blood products and evaluate client response
- Access venous access devices, including tunneled, implanted, and central lines
- Perform calculations needed for medication administration
- Evaluate client response to medication (e.g., therapeutic effects, side effects, adverse reactions)
- Educate the client about medications
- Prepare and administer medications, using rights of medication administration
- Review pertinent data prior to medication administration (e.g., contraindications, lab results, allergies, potential interactions)
- Participate in the medication reconciliation process
- Titrate the dosage of medication based on assessment and ordered parameters (e.g., giving insulin according to blood glucose levels, titrating medication to maintain specific blood pressure)
- Evaluate appropriateness and accuracy of medication order for the client
- Monitor intravenous infusion and maintain the site (e.g., central, PICC, epidural, and venous access devices)
- Administer pharmacological measures for pain management
- Administer controlled substances within regulatory guidelines (e.g., witness, waste)
- Administer parenteral nutrition and evaluate client response (e.g., TPN)
Some of the commonly used terms and terminology relating to pharmacological and parenteral treatments that you must be aware of and knowledgeable about include those briefly described below:
- Pharmacokinetics: Pharmacokinetics is the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion of drugs.
- Pharmacodynamics: Pharmacodynamics refers to the actions of medications in the body. Drug concentrations, receptor and binding activities, antagonistic actions, and agonist actions are pharmacodynamic principles.
- Drug absorption: Drug absorption is the pharmacokinetic process by which the medication moves through the body to the bloodstream. Because intravenous medications are delivered directly into the bloodstream, they are not absorbed. The rates of absorption for oral medications vary according to the acidity of the stomach's fluids, the presence of food, and other factors.
- Drug distribution: Drug distribution, the second phase of the pharmacokinetic process, is the movement of the medication through the bloodstream to its target. Fat-soluble medications are attracted to fatty tissue targets.
- Drug metabolism or biotransformation: Drug metabolism, also referred to as biotransformation, is the third phase of the pharmacokinetic process. Drug metabolism is defined as the detoxification and breaking down of drugs in the liver.
- Excretion: Excretion, the final stage of pharmacokinetics, is defined as the elimination of active and inactive drug metabolites from the body. The vast majority of medications are excreted by the kidney and the urinary tract but some may be excreted via the respiratory and gastrointestinal tract.
- Indications for medications: The indications for medications are those diseases, disorders, illnesses, and conditions that are appropriate uses for a particular medication. For example, the indications for the use of phenobarbital include the control of seizures, the prevention of seizures, decrease anxiety and withdrawal from a barbiturate. The indications for medications are established by the United States Food and Drug Administration. When a medication is used for any other than these established and approved uses, this usage is referred to as an "off-label use".
- Contraindications of medications: Virtually all medications are not indicated for, and thus, contraindicated for certain clients, based on one or more conditions. For example, medications classified as Categories C, D, and X are contraindicated for women who are pregnant. Many drugs are contraindicated during pregnancy, during lactation, and when the client has a history of renal or hepatic disease, for example.
- The cautious use of medications: Like contraindications, many medications have published precautions that indicate the cautious use of medication based on the status of the client; although the cautious use of a medication is often done, it is done when there are no suitable alternatives to it with the provision that the client will be closely monitored and assessed for any adverse effects.
- Therapeutic effects of medication: A therapeutic effect is the desired effect of the specific medication. For example, the therapeutic and desired effects of anti-anxiety medications are to decrease the client's level of anxiety and the therapeutic effects of anti-hypertensive medications are to decrease the client's blood pressure.
- Side effects of medication: A side effect of a medication is any effect(s) other than the therapeutic and intended effect(s) of a medication. Some side effects adversely affect a client, other side effects can be harmless to the client, and still, more may be desirable side effect that is therapeutic for the client. These kinds of side effects can include damage to the 8th cranial nerve, minor oral dryness, and sleepiness after taking an antihistamine such as diphenhydramine which is taken by many people, particularly the elderly, to induce sleep rather than for its antihistamine actions.
- Idiosyncratic effects of medication: Idiosyncratic effects of the medication include those side effects that are rare, unusual, and unexpected. These effects can include things like a client experiencing hyperactivity after having taken a sedating medication. These effects tend to be individual rather than common to a group or population of clients affected with a certain risk factor of disorder, for example.
- Cumulative effects of medication: The cumulative effects of a medication are those effects that result from the accumulation of a medication. Cumulative effects of medications can occur as the result of several impaired pharmacokinetic processes including the impaired biotransformation and excretion of drugs, as often occurs among elderly clients because of some of the normal changes in the aging process. At times, the cumulative effects of a medication can be a life-threatening overdose of the medication; therefore, caution must be exercised when a client is at risk for the accumulation of a medication and its cumulative effects.
- Adverse effects of medication: The adverse effect of a medication is highly serious and far more troublesome than the side effects of medications. For example, an anaphylactic response to an antibiotic is an adverse effect of that medication. Except under highly unusual circumstances, medications that lead to adverse effects are immediately discontinued.
- Drug interactions: Drug interactions occur when drugs and foods interact, when drugs and herbs or supplements interact, and when drugs and other drugs interact. Some of these drug interactions are synergistic and potentiating and others may be inhibiting.
- Potentiating effects of medication: A potentiating effect of a medication is the synergistic, additive effect that occurs when drugs and foods interact, when drugs and herbs or supplements interact, and when drugs and other drugs interact. The former two interactions will make the medication more powerful in its effects, and the latter will have an increased effect by one or more of the medications that are interacting.
- Inhibiting effects of medication: An inhibiting effect of a medication is a decreased effect that occurs when drugs and foods interact, when drugs and herbs or supplements interact, and when drugs and other drugs interact. The former two interactions will weaken the effects of the medication, and the latter will have a decreased and inhibiting effect on one or more of the medications that are interacting.
- Drug toxicity: Drug toxicity is defined as overdosage of a medication that occurs when the dose that is administered exceeds the client's ability to metabolize and/or excrete the medication.
- Drug allergy: A drug allergy is the result of an antigen-antibody immunologic response to a medication. All clients must be assessed for any drug sensitivities and allergies.
- Drug tolerance: Drug tolerance occurs when a client has been receiving a particular medication, such as an opioid drug, for a prolonged period of time and, as a result of this prolonged administration, the client needs increasing doses of the medication to produce the therapeutic effect.
- The chemical name of a drug: The chemical name of a drug is the chemical composition of the drug.
- The trade or brand name of a drug: The trade or brand name of a drug is the manufacturer's name for the drug. Trade name drugs are more expensive than generic drugs.
- The generic name of a drug: The generic name of a drug is the name of a drug that is given to it by the United States Adopted Names Council. This name remains the same over time. A generic medication can have a number of different trade names, but a trade name is the exclusive property of the drug manufacturer, therefore, there is no more than one trade name. For example, the generic name of metoprolol can have multiple trade names such as Metoprolol Succinate and Lopressor, both of which are capitalized, unlike generic names.
Related content includes but is not limited to:
- Adverse Effects/Contraindications/Side Effects/Interactions
- Blood and Blood Products
- Central Venous Access Devices
- Dosage Calculations
- Expected Actions/Outcomes
- Medication Administration
- Parenteral/Intravenous Therapies
- Pharmacological Pain Management
- Total Parenteral Nutrition (TPN)
Explore – Pharmacological & Parenteral Therapies Practice Test Questions
Reduction of Risk Potential
The Reduction of Risk Potential questions will test the ability of the nurse to reduce the likelihood that clients will develop complications or health problems related to existing conditions, treatments, or procedures.
The nurse must be able to:
- Assess and respond to changes in the client’s vital signs
- Perform diagnostic testing (e.g., electrocardiogram, oxygen saturation, glucose monitoring)
- Monitor the results of diagnostic testing and intervene as needed
- Obtain blood specimens peripherally or through the central line
- Obtain specimens other than blood for diagnostic testing (e.g., wound, stool, urine)
- Insert, maintain and remove a gastric tube
- Insert, maintain and remove a urinary catheter
- Insert, maintain and remove a peripheral intravenous line
- Use precautions to prevent injury and/or complications associated with a procedure or diagnosis
- Evaluate responses to procedures and treatments
- Recognize trends and changes in client condition and intervene as needed
- Perform focused assessment
- Educate the client about treatments and procedures
- Provide preoperative and postoperative education
- Provide preoperative care
- Provide intraoperative care
- Manage client during and following a procedure with moderate sedation
Related content includes but is not limited to:
- Changes/Abnormalities in Vital Signs
- Diagnostic Tests
- Laboratory Values
- Potential For Alterations in Body Systems
- Potential for Complications of Diagnostic Tests/Treatments/ Procedures
- Potential for Complications from Surgical Procedures and Health Alterations
- System Specific Assessments
- Therapeutic Procedures
Explore – Reduction of Risk Potential Practice Test Questions
Physiological Adaptation
The Physiological Adaptation questions will test the ability of the nurse to manage and provide care for clients with acute, chronic, or life-threatening physical health conditions.
The nurse is expected to be able to:
- Assist with invasive procedures (e.g., central line, thoracentesis, bronchoscopy)
- Implement and monitor phototherapy
- Maintain an optimal temperature for the client (e.g., cooling and/or warming blanket)
- Monitor and care for clients on a ventilator
- Monitor and maintain devices and equipment used for drainage (e.g., surgical wound drains, chest tube suction, negative pressure wound therapy)
- Perform and manage the care of clients receiving peritoneal dialysis
- Perform suctioning (e.g. oral, nasopharyngeal, endotracheal, tracheal)
- Provide wound care or dressing change
- Provide ostomy care and education (e.g. tracheal, enteral)
- Provide pulmonary hygiene (e.g., chest physiotherapy, incentive spirometry)
- Provide postoperative care
- Manage the care of a client with a fluid and electrolyte imbalance
- Monitor and maintain arterial lines
- Manage the care of a client with a pacing device (e.g., pacemaker)
- Manage the care of a client on telemetry
- Manage the care of a client receiving hemodialysis
- Manage the care of a client with alteration in hemodynamics, tissue perfusion, and hemostasis (e.g., cerebral, cardiac, peripheral)
- Educate the client regarding an acute or chronic condition
- Manage the care of a client with impaired ventilation/oxygenation
- Evaluate the effectiveness of the treatment regimen for a client with an acute or chronic diagnosis
- Perform emergency care procedures (e.g., cardio-pulmonary resuscitation, respiratory support, automated external defibrillator)
- Identify pathophysiology related to an acute or chronic condition (e.g., signs and symptoms)
- Recognize the signs and symptoms of complications and intervene appropriately when providing client care
Related content includes, but is not limited to:
- Alterations in Body Systems
- Fluid and Electrolyte Imbalances
- Hemodynamics
- Illness Management
- Medical Emergencies
- Pathophysiology
- Unexpected Responses to Therapies
Explore – Physiological Adaptation Practice Test Questions
PLEASE NOTE: National Council Licensure Examination (NCLEX-RN®) is a registered trademark of the National Council of State Boards of Nursing, Inc. None of the trademark holders are affiliated with RegisteredNursing.org.
Latest Articles & Guides
One of the keys to success as a registered nurse is embracing lifelong learning. Our articles and guides address hot topics and current events in nursing, from education to career mobility and beyond. No matter where you are on your nursing journey, there’s an article to help you build your knowledge base.
Browse our latest articles, curated specifically for modern nurses.



